Page 48 - PEN eBook July 2023
P. 48
Design
To test bidirectional switching, Figure 4 illustrates the circuit schematics for the specific current
direction. Low-R cascode MOSFETs are used to drive B-TRAN as a normally off switch like an
DS(on)
IGBT. These devices can block high voltage in their off state and conduct high current with low loss
in their on state.
“Our conduction losses are less than half of the conventional semiconductors,” Brdar said. “We
actually enable applications like a solid-state circuit breaker, where conduction losses really drive
the design.” Inductor L1 and fast-recovery diode D1 are connected across the inductor as part of
the DPT.
B-TRAN CHARACTERIZATION
Initial measurements of B-TRAN dies
and packaged devices are conducted
using a Keithley high-power test
system. Breakdown voltage and
leakage current are measured by
ramping up the voltage across the
device while monitoring the current.
A breakdown voltage of 1,280 V is
measured, and leakage currents are
measured to be 25 µA at 1,000 V and
45 µA at 1,200 V, which confirms
the basic steady-state performance
parameters. The emitter-emitter
saturation voltage and current gain
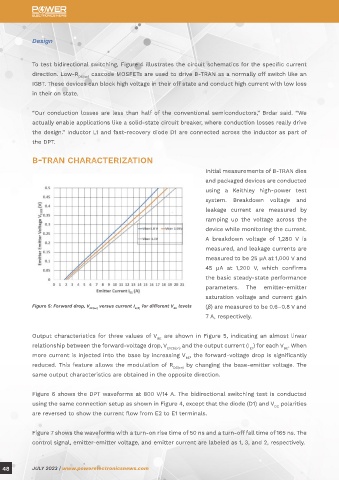
Figure 5: Forward drop, V versus current I for different V levels (β) are measured to be 0.6–0.8 V and
EE(on) E(A) BE
7 A, respectively.
Output characteristics for three values of V are shown in Figure 5, indicating an almost linear
BE
relationship between the forward-voltage drop, V and the output current (I ) for each V . When
E1E2(on) E1 BE
more current is injected into the base by increasing V , the forward-voltage drop is significantly
BE
reduced. This feature allows the modulation of R by changing the base-emitter voltage. The
DS(on)
same output characteristics are obtained in the opposite direction.
Figure 6 shows the DPT waveforms at 800 V/14 A. The bidirectional switching test is conducted
using the same connection setup as shown in Figure 4, except that the diode (D1) and V polarities
DC
are reversed to show the current flow from E2 to E1 terminals.
Figure 7 shows the waveforms with a turn-on rise time of 50 ns and a turn-off fall time of 165 ns. The
control signal, emitter-emitter voltage, and emitter current are labeled as 1, 3, and 2, respectively.
48 JULY 2023 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com