Page 13 - PEN eBook July 2022
P. 13
THERMAL MANAGEMENT Thermal Management
To achieve the required higher power density, the following three main contributors must be
considered:
▶ Increased efficiency to maintain an acceptable total power loss in a given volume. This
drives the transition to new topologies and technologies. A great example is the transition
from the conventional silicon classic-boost PFC to the gallium nitride/silicon carbide
totem-pole PFC.
▶ Improved packages and thermal solutions that can dissipate the power away from
the device junction to
heatsinks and ambient.
This becomes more
challenging in smaller
surface-mount device
(SMD) packages that are
the main enabler for
high-density converters.
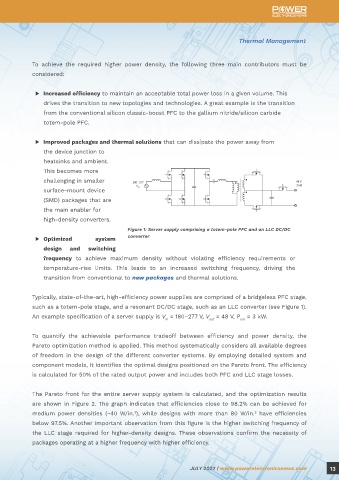
Packaging and ▶ Optimized system Figure 1: Server supply comprising a totem-pole PFC and an LLC DC/DC
converter
Thermal Solutions to design and switching
frequency to achieve maximum density without violating efficiency requirements or
Fulfill Trends in Data temperature-rise limits. This leads to an increased switching frequency, driving the
transition from conventional to new packages and thermal solutions.
Centers and Server SMPS Typically, state-of-the-art, high-efficiency power supplies are comprised of a bridgeless PFC stage,
such as a totem-pole stage, and a resonant DC/DC stage, such as an LLC converter (see Figure 1).
An example specification of a server supply is V = 180–277 V, V = 48 V, P = 3 kW.
out
out
in
How to meet the design requirements
of power supplies using silicon and To quantify the achievable performance tradeoff between efficiency and power density, the
Pareto optimization method is applied. This method systematically considers all available degrees
wide-bandgap switches of freedom in the design of the different converter systems. By employing detailed system and
component models, it identifies the optimal designs positioned on the Pareto front. The efficiency
By Daniel Hölzl, package concept engineer, and Sam Abdel-Rahman, system is calculated for 50% of the rated output power and includes both PFC and LLC stage losses.
architect for server/data center SMPS, both at Infineon Technologies
The Pareto front for the entire server supply system is calculated, and the optimization results
are shown in Figure 2. The graph indicates that efficiencies close to 98.2% can be achieved for
The emergence of cloud-based internet services, artificial intelligence, and cryptocurrency has medium power densities (~40 W/in. ), while designs with more than 80 W/in. have efficiencies
3
3
initiated a strong growth of processing power in data centers worldwide. In combination with rising below 97.5%. Another important observation from this figure is the higher switching frequency of
electricity and real estate prices, this trend creates a clear need for highly efficient and compact the LLC stage required for higher-density designs. These observations confirm the necessity of
server power supplies. packages operating at a higher frequency with higher efficiency.
12 JULY 2022 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com JULY 2022 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com 13