Page 56 - EE Times Europe Magazine | February 2020
P. 56
54 EE|Times EUROPE
AUTOMOTIVE POWER
Galvanic Isolation in EV and HEV Applications
By Maurizio Di Paolo Emilio
he worldwide proliferation of electric
and hybrid electric vehicles (EVs and
HEVs), which must withstand higher
T operating voltages and currents than
gasoline-powered vehicles, has underscored
the importance of electrical isolation for
automotive design. Electrifi cation of the car
has mandated the use of high-power devices
— notably batteries, inverters, and regenera-
tive braking systems — whose interfacing with
digital control circuits requires the adoption
of appropriate galvanic isolation techniques.
Electrical, or galvanic, isolation is the con-
dition in which no direct current circulation
takes place between two points of differing
electrical potential. More precisely, it is not
possible to move charge carriers from one
point to another while electrical energy (or
a signal) can still be exchanged by other
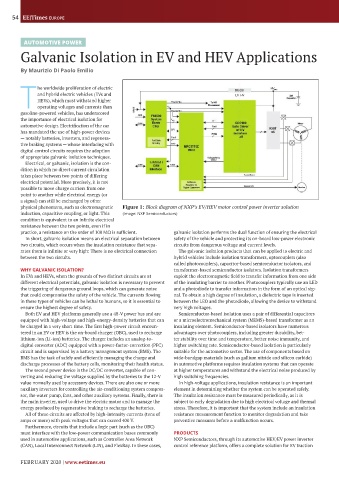
physical phenomena, such as electromagnetic Figure 1: Block diagram of NXP’s EV/HEV motor control power inverter solution
induction, capacitive coupling, or light. This (Image: NXP Semiconductors)
condition is equivalent to an infi nite electrical
resistance between the two points, even if in
practice, a resistance on the order of 100 M is suffi cient. galvanic isolation performs the dual function of ensuring the electrical
In short, galvanic isolation means an electrical separation between safety of the vehicle and protecting its on-board low-power electronic
two circuits, which occurs when the insulation resistance that sepa- circuits from dangerous voltage and current levels.
rates them is infi nite or very high There is no electrical connection The galvanic isolation products that can be applied to electric and
between the two circuits. hybrid vehicles include isolation transformers, optocouplers (also
called photocouplers), capacitor-based semiconductor isolators, and
WHY GALVANIC ISOLATION? transformer-based semiconductor isolators. Isolation transformers
In EVs and HEVs, when the grounds of two distinct circuits are at exploit the electromagnetic fi eld to transfer information from one side
different electrical potentials, galvanic isolation is necessary to prevent of the insulating barrier to another. Photocouplers typically use an LED
the triggering of dangerous ground loops, which can generate noise and a photodiode to transfer information in the form of an optical sig-
that could compromise the safety of the vehicle. The currents fl owing nal. To obtain a high degree of insulation, a dielectric tape is inserted
in these types of vehicles can be lethal to humans, so it is essential to between the LED and the photodiode, allowing the device to withstand
ensure the highest degree of safety. very high voltages.
Both EV and HEV platforms generally use a 48-V power bus and are Semiconductor-based isolation uses a pair of differential capacitors
equipped with high-voltage and high-energy-density batteries that can or a microelectromechanical system (MEMS)-based transformer as an
be charged in a very short time. The fi rst high-power circuit encoun- insulating element. Semiconductor-based isolators have numerous
tered in an EV or HEV is the on-board charger (OBC), used to recharge advantages over photocouplers, including greater durability, bet-
lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. The charger includes an analog-to- ter stability over time and temperature, better noise immunity, and
digital converter (ADC) equipped with a power-factor-correction (PFC) higher switching rate. Semiconductor-based isolation is particularly
circuit and is supervised by a battery management system (BMS). The suitable for the automotive sector. The use of components based on
BMS has the task of safely and effi ciently managing the charge and wide-bandgap materials (such as gallium nitride and silicon carbide)
discharge processes of the battery cells, monitoring their health status. in automotive platforms requires insulation systems that can operate
The second power device is the DC/DC converter, capable of con- at higher temperatures and withstand the electrical noise produced by
verting and reducing the voltage supplied by the batteries to the 12-V high switching frequencies.
value normally used by accessory devices. There are also one or more In high-voltage applications, insulation resistance is an important
auxiliary inverters for controlling the air-conditioning system compres- element in determining whether the system can be operated safely.
sor, the water pump, fans, and other auxiliary systems. Finally, there is The insulation resistance must be measured periodically, as it is
the main inverter, used to drive the electric motor and to manage the subject to early degradation due to high electrical voltage and thermal
energy produced by regenerative braking to recharge the batteries. stress. Therefore, it is important that the system include an insulation
All of these circuits are affected by high-intensity currents (tens of resistance measurement function to monitor degradation and take
amps or more) with peak voltages that can exceed 400 V. preventive measures before a malfunction occurs.
Furthermore, circuits that include a logic part (such as the OBC)
must interface with the low-power communication buses commonly PRODUCTS
used in automotive applications, such as Controller Area Network NXP Semiconductors, through its automotive HEV/EV power inverter
(CAN), Local Interconnect Network (LIN), and FlexRay. In these cases, control reference platform, offers a complete solution for EV traction
FEBRUARY 2020 | www.eetimes.eu