Page 9 - PEN eBook October2023
P. 9
Cover Story — Design
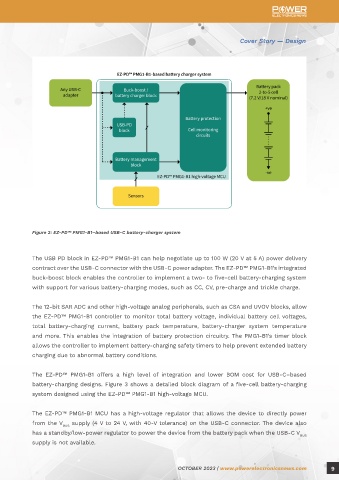
Figure 2: EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1–based USB-C battery-charger system
The USB PD block in EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 can help negotiate up to 100 W (20 V at 5 A) power delivery
contract over the USB-C connector with the USB-C power adapter. The EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1’s integrated
buck-boost block enables the controller to implement a two- to five-cell battery-charging system
with support for various battery-charging modes, such as CC, CV, pre-charge and trickle charge.
The 12-bit SAR ADC and other high-voltage analog peripherals, such as CSA and UVOV blocks, allow
the EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 controller to monitor total battery voltage, individual battery cell voltages,
total battery-charging current, battery pack temperature, battery-charger system temperature
and more. This enables the integration of battery protection circuitry. The PMG1-B1’s timer block
allows the controller to implement battery-charging safety timers to help prevent extended battery
charging due to abnormal battery conditions.
The EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 offers a high level of integration and lower BOM cost for USB-C–based
battery-charging designs. Figure 3 shows a detailed block diagram of a five-cell battery-charging
system designed using the EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 high-voltage MCU.
The EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 MCU has a high-voltage regulator that allows the device to directly power
from the V supply (4 V to 24 V, with 40-V tolerance) on the USB-C connector. The device also
BUS
has a standby/low-power regulator to power the device from the battery pack when the USB-C V
BUS
supply is not available.
OCTOBER 2023 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com 9