Page 8 - PEN eBook October2023
P. 8
Cover Story — Design
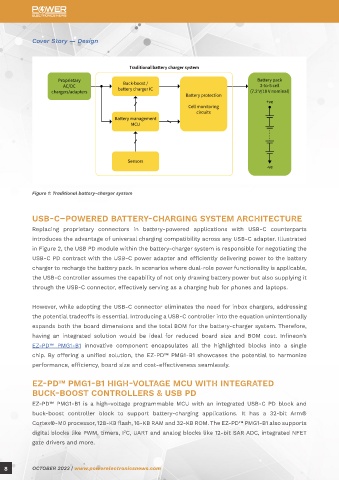
Figure 1: Traditional battery-charger system
USB-C–POWERED BATTERY-CHARGING SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Replacing proprietary connectors in battery-powered applications with USB-C counterparts
introduces the advantage of universal charging compatibility across any USB-C adapter. Illustrated
in Figure 2, the USB PD module within the battery-charger system is responsible for negotiating the
USB-C PD contract with the USB-C power adapter and efficiently delivering power to the battery
charger to recharge the battery pack. In scenarios where dual-role power functionality is applicable,
the USB-C controller assumes the capability of not only drawing battery power but also supplying it
through the USB-C connector, effectively serving as a charging hub for phones and laptops.
However, while adopting the USB-C connector eliminates the need for inbox chargers, addressing
the potential tradeoffs is essential. Introducing a USB-C controller into the equation unintentionally
expands both the board dimensions and the total BOM for the battery-charger system. Therefore,
having an integrated solution would be ideal for reduced board size and BOM cost. Infineon’s
EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 innovative component encapsulates all the highlighted blocks into a single
chip. By offering a unified solution, the EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 showcases the potential to harmonize
performance, efficiency, board size and cost-effectiveness seamlessly.
EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 HIGH-VOLTAGE MCU WITH INTEGRATED
BUCK-BOOST CONTROLLERS & USB PD
EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 is a high-voltage programmable MCU with an integrated USB-C PD block and
buck-boost controller block to support battery-charging applications. It has a 32-bit Arm®
Cortex®-M0 processor, 128-KB flash, 16-KB RAM and 32-KB ROM. The EZ-PD™ PMG1-B1 also supports
digital blocks like PWM, timers, I C, UART and analog blocks like 12-bit SAR ADC, integrated NFET
2
gate drivers and more.
8 OCTOBER 2023 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com