Page 15 - PEN eBook December 2022
P. 15
POWER SUPPLIES Power Supplies
Reduced volume not only enhances the user experience, but it also lowers manufacturing and delivery
expenses. To achieve higher power densities, a common practice is to increase the switching frequency,
3
which also helps to reduce the size of both inductors and capacitors. Operating at a higher frequency,
4,5
however, affects the overall efficiency and thermal management. As a result, power inductors should
be able to work under a large current with minimal power loss.
On the market, there are two main types of power inductors: ferrite and metal composite. Due
to its high permeability, wire-wound ferrite is an ideal choice for high-inductance applications.
However, its small saturation flux density limits the size reduction of power inductors and involves
thermal management issues. On the other hand, a higher saturation flux density is provided by
a metal-composite–type inductor, usually built with alloy powder and organic binders with coil
molded inside. At a higher temperature, however, performance deteriorates due to the presence of
organic resin, while power losses are higher than in a ferrite inductor.
THE NOVEL INDUCTOR DESIGN
A Novel Inductor Design The new inductor employs as magnetic material an Fe-based alloy powder named NPA-F, characterized
by low loss and high saturation. The material is manufactured in a spherical shape using the gas
Boosts Efficiency in atomization method. That ensures low eddy current loss even at high frequency and protects against
insulation layer cracking.
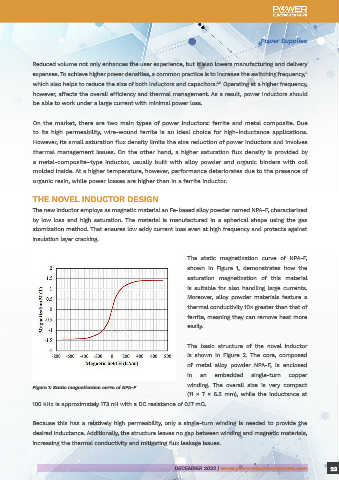
DC/DC Converters The static magnetization curve of NPA-F,
shown in Figure 1, demonstrates how the
saturation magnetization of this material
By Stefano Lovati, technical writer for EEWeb
is suitable for also handling large currents.
Moreover, alloy powder materials feature a
The inductor is a key component in DC/DC converters due to its ability to suppress the AC ripple thermal conductivity 10× greater than that of
current, providing in output a smoothed DC current. The latest-generation electronic devices are ferrite, meaning they can remove heat more
extremely compact and with increasingly advanced features. Usually battery-powered, they require high easily.
energy efficiency, starting with basic components like inductors found in DC/DC converters. Because
the efficiency of an inductor is strictly dependent on the core and winding losses, it shall absorb ripple The basic structure of the novel inductor
current while minimizing losses. is shown in Figure 2. The core, composed
of metal alloy powder NPA-F, is enclosed
This article will present a novel power inductor design to be used in compact and large current in an embedded single-turn copper
DC/DC converters, suitable to operate even at high frequencies. This inductor, based on an iron winding. The overall size is very compact
Figure 1: Static magnetization curve of NPA-F
(Fe)-based alloy powder, exhibits excellent performance with increased efficiency and smaller size (11 × 7 × 6.5 mm), while the inductance at
compared with a conventional ferrite inductor. Read the original article here. 6 100 kHz is approximately 173 nH with a DC resistance of 0.17 mΩ.
PERFORMANCE VS. SIZE Because this has a relatively high permeability, only a single-turn winding is needed to provide the
Today, engineers are demanded to design smaller power supplies with improved efficiency for desired inductance. Additionally, the structure leaves no gap between winding and magnetic materials,
powering ICs like FPGAs and GPUs, which notoriously operate at a lower voltage and larger current. increasing the thermal conductivity and mitigating flux leakage issues.
1,2
22 DECEMBER 2022 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com DECEMBER 2022 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com 23