Page 31 - 23_EETE_03
P. 31
EE|Times EUROPE 31
Green Electricity Key to Eliminating Transportation CO 2
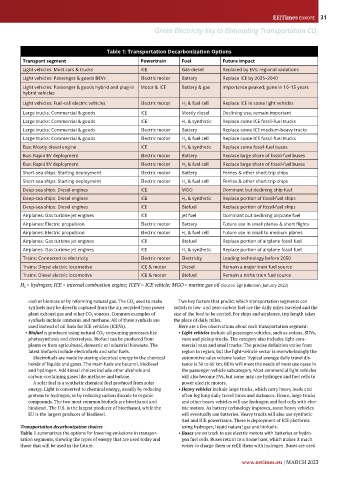
Table 1: Transportation Decarbonization Options
Transport segment Powertrain Fuel Future impact
Light vehicles: Most cars & trucks ICE Gas-diesel Replaced by EVs; regional variations
Light vehicles: Passenger & goods BEVs Electric motor Battery Replace ICE by 2035–2040
Light vehicles: Passenger & goods hybrid and plug-in Motor & ICE Battery & gas Importance peaked; gone in 10–15 years
hybrid vehicles
Light vehicles: Fuel-cell electric vehicles Electric motor H 2 & fuel cell Replace ICE in some light vehicles
Large trucks: Commercial & goods ICE Mostly diesel Declining use; remain important
Large trucks: Commercial & goods ICE H 2 & synthetic Replace some ICE fossil-fuel trucks
Large trucks: Commercial & goods Electric motor Battery Replace some ICE medium-heavy trucks
Large trucks: Commercial & goods Electric motor H 2 & fuel cell Replace some ICE fossil-fuel trucks
Bus: Mostly diesel engine ICE H 2 & synthetic Replace some fossil-fuel buses
Bus: Rapid EV deployment Electric motor Battery Replace large share of fossil-fuel buses
Bus: Rapid EV deployment Electric motor H 2 & fuel cell Replace large share of fossil-fuel buses
Short-sea ships: Starting deployment Electric motor Battery Ferries & other short-trip ships
Short-sea ships: Starting deployment Electric motor H 2 & fuel cell Ferries & other short-trip ships
Deep-sea ships: Diesel engines ICE MGO Dominant but declining ship fuel
Deep-sea ships: Diesel engines ICE H 2 & synthetic Replace portion of fossil-fuel ships
Deep-sea ships: Diesel engines ICE Biofuel Replace portion of fossil-fuel ships
Airplanes: Gas turbine jet engines ICE Jet fuel Dominant but declining airplane fuel
Airplanes: Electric propulsion Electric motor Battery Future use in small planes & short flights
Airplanes: Electric propulsion Electric motor H 2 & fuel cell Future use in small to medium planes
Airplanes: Gas turbine jet engines ICE Biofuel Replace portion of airplane fossil fuel
Airplanes: Gas turbine jet engines ICE H 2 & synthetic Replace portion of airplane fossil fuel
Trains: Connected to electricity Electric motor Electricity Leading technology before 2050
Trains: Diesel electric locomotive ICE & motor Diesel Remain a major train fuel source
Trains: Diesel electric locomotive ICE & motor Biofuel Remain a niche train fuel source
H 2 = hydrogen; ICE = internal combustion engine; ICEV = ICE vehicle; MGO = marine gas oil (Source: Egil Juliussen, January 2023)
coal or biomass or by reforming natural gas. The CO 2 used to make Two key factors that predict which transportation segments can
synfuels may be directly captured from the air, recycled from power switch to low- and zero-carbon fuel are the daily miles traveled and the
plant exhaust gas and other CO 2 sources. Common examples of size of the load to be carried. For ships and airplanes, trip length takes
synfuels include ammonia and methane. All of these synfuels are the place of daily miles.
used instead of oil fuels for ICE vehicles (ICEVs). Here are a few observations about each transportation segment:
• Biofuel is produced using natural CO 2 -consuming processes like • Light vehicles include all passenger vehicles, such as sedans, SUVs,
photosynthesis and electrolysis. Biofuel can be produced from vans and pickup trucks. The category also includes light com-
plants or from agricultural, domestic or industrial biowaste. The mercial vans and small trucks. The precise definition varies from
latest biofuels include electrofuels and solar fuels. region to region, but the light-vehicle sector is overwhelmingly the
Electrofuels are made by storing electrical energy in the chemical automotive sales volume leader. Typical average daily travel dis-
bonds of liquids and gases. The main fuels are butanol, biodiesel tance is 30 to 60 km. BEVs will meet the needs of most use cases in
and hydrogen. Additional choices include other alcohols and the passenger-vehicle subcategory. Most commercial light vehicles
carbon-containing gases like methane and butane. will also become EVs, but some may use hydrogen and fuel cells to
A solar fuel is a synthetic chemical fuel produced from solar power electric motors.
energy. Light is converted to chemical energy, usually by reducing • Heavy vehicles include large trucks, which carry heavy loads and
protons to hydrogen, or by reducing carbon dioxide to organic often log long daily travel times and distances. Hence, large trucks
compounds. The two most common biofuels are bioethanol and and other heavy vehicles will use hydrogen and fuel cells with elec-
biodiesel. The U.S. is the largest producer of bioethanol, while the tric motors. As battery technology improves, some heavy vehicles
EU is the largest producer of biodiesel. will eventually use batteries. Heavy trucks will also use synthetic
fuel and ICE powertrains. There is deployment of ICE platforms
Transportation decarbonization choices using hydrogen, liquid natural gas and biofuels.
Table 1 summarizes the options for lowering emissions in transpor- • Buses are on track to use electric motors with batteries or hydro-
tation segments, showing the types of energy that are used today and gen fuel cells. Buses return to a home base, which makes it much
those that will be used in the future. easier to charge them or refill them with hydrogen. Buses are used
www.eetimes.eu | MARCH 2023