Page 51 - 23_EETE_03
P. 51
EE|Times EUROPE 51
Key Technological Challenges Loom for 6G Development
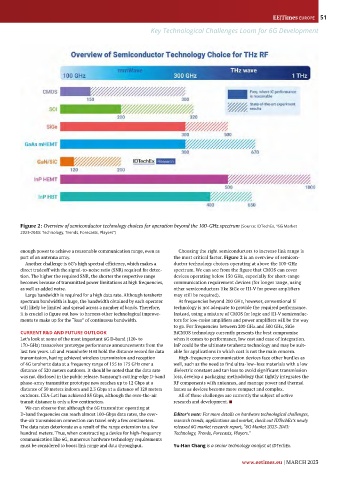
Figure 2: Overview of semiconductor technology choices for operation beyond the 100-GHz spectrum (Source: IDTechEx, “6G Market
2023-2043: Technology, Trends, Forecasts, Players”)
enough power to achieve a reasonable communication range, even as Choosing the right semiconductors to increase link range is
part of an antenna array. the most critical factor. Figure 2 is an overview of semicon-
Another challenge is 6G’s high spectral efficiency, which makes a ductor technology choices operating at above the 100-GHz
direct tradeoff with the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) required for detec- spectrum. We can see from the figure that CMOS can cover
tion. The higher the required SNR, the shorter the respective range devices operating below 150 GHz, especially for short-range
becomes because of transmitted power limitations at high frequencies, communication requirement devices (for longer range, using
as well as added noise. other semiconductors like SiGe or III-V for power amplifiers
Large bandwidth is required for a high data rate. Although terahertz may still be required).
spectrum bandwidth is huge, the bandwidth obtained by each operator At frequencies beyond 200 GHz, however, conventional Si
will likely be limited and spread across a number of bands. Therefore, technology is not adequate to provide the required performance.
it is crucial to figure out how to harness other technological improve- Instead, using a mixture of CMOS for logic and III-V semiconduc-
ments to make up for the “loss” of continuous bandwidth. tors for low-noise amplifiers and power amplifiers will be the way
to go. For frequencies between 200 GHz and 500 GHz, SiGe
CURRENT R&D AND FUTURE OUTLOOK BiCMOS technology currently presents the best compromise
Let’s look at some of the most important 6G D-band (120- to when it comes to performance, low cost and ease of integration.
170-GHz) transceiver prototype performance announcements from the InP could be the ultimate terahertz technology and may be suit-
last two years. LG and Fraunhofer HHI hold the distance record for data able for applications in which cost is not the main concern.
transmission, having achieved wireless transmission and reception High-frequency communication devices face other hurdles as
of 6G terahertz data at a frequency range of 155 to 175 GHz over a well, such as the need to find ultra-low–loss materials with a low
distance of 320 meters outdoors. It should be noted that the data rate dielectric constant and tan loss to avoid significant transmission
was not disclosed in the public release. Samsung’s cutting-edge D-band loss, develop a packaging methodology that tightly integrates the
phase-array transmitter prototype now reaches up to 12 Gbps at a RF components with antennas, and manage power and thermal
distance of 30 meters indoors and 2.3 Gbps at a distance of 120 meters issues as devices become more compact and complex.
outdoors. CEA-Leti has achieved 85 Gbps, although the over-the-air All of these challenges are currently the subject of active
transit distance is only a few centimeters. research and development. ■
We can observe that although the 6G transmitter operating at
D-band frequencies can reach almost 100-Gbps data rates, the over- Editor’s note: For more details on hardware technological challenges,
the-air transmission connection can travel only a few centimeters. research trends, applications and market, check out IDTechEx’s newly
The data rates deteriorate as a result of the range extension to a few released 6G market research report, “6G Market 2023-2043:
hundred meters. Thus, when constructing a device for high-frequency Technology, Trends, Forecasts, Players.”
communication like 6G, numerous hardware technology requirements
must be considered to boost link range and data throughput. Yu-Han Chang is a senior technology analyst at IDTechEx.
www.eetimes.eu | MARCH 2023