Page 17 - PEN eBook July 2023
P. 17
Smart Energy
PRINCIPLE & TYPES OF POWER BATTERIES
The first distinction that can be made between batteries is that there are primary and secondary
batteries. Primary batteries are non-chargeable, whereas secondary batteries are rechargeable.
Each battery system is characterized by its chemistry, and there are many varieties of power
batteries on the market. Because the focus of this article is mainly on secondary batteries, the
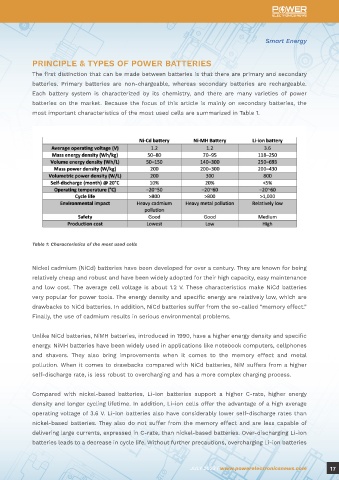
most important characteristics of the most used cells are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Characteristics of the most used cells
Nickel cadmium (NiCd) batteries have been developed for over a century. They are known for being
relatively cheap and robust and have been widely adopted for their high capacity, easy maintenance
and low cost. The average cell voltage is about 1.2 V. These characteristics make NiCd batteries
very popular for power tools. The energy density and specific energy are relatively low, which are
drawbacks to NiCd batteries. In addition, NiCd batteries suffer from the so-called “memory effect.”
Finally, the use of cadmium results in serious environmental problems.
Unlike NiCd batteries, NiMH batteries, introduced in 1990, have a higher energy density and specific
energy. NiMH batteries have been widely used in applications like notebook computers, cellphones
and shavers. They also bring improvements when it comes to the memory effect and metal
pollution. When it comes to drawbacks compared with NiCd batteries, NiM suffers from a higher
self-discharge rate, is less robust to overcharging and has a more complex charging process.
Compared with nickel-based batteries, Li-ion batteries support a higher C-rate, higher energy
density and longer cycling lifetime. In addition, Li-ion cells offer the advantage of a high average
operating voltage of 3.6 V. Li-ion batteries also have considerably lower self-discharge rates than
nickel-based batteries. They also do not suffer from the memory effect and are less capable of
delivering large currents, expressed in C-rate, than nickel-based batteries. Over-discharging Li-ion
batteries leads to a decrease in cycle life. Without further precautions, overcharging Li-ion batteries
JULY 2023 | www.powerelectronicsnews.com 17