Page 42 - 23_EETE_03
P. 42
42 EE|Times EUROPE
QUANTUM COMPUTING
The Status of Room-Temperature Quantum
Computers
By Tess Skyrme, IDTechEx
uantum computers promise to master problems that would improve accessibility to quantum computing and ultimately result in a
take classical computers trillions of years to solve. Stand- larger addressable market.
ing in the way of broad deployment, however, is that most
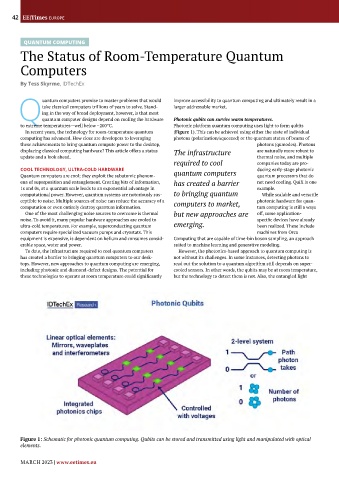
Qquantum computer designs depend on cooling the hardware Photonic qubits can survive warm temperatures.
to extreme temperatures—well below –200°C. Photonic platform quantum computing uses light to form qubits
In recent years, the technology for room-temperature quantum (Figure 1). This can be achieved using either the state of individual
computing has advanced. How close are developers to leveraging photons (polarization/squeezed) or the quantum states of beams of
these achievements to bring quantum compute power to the desktop, photons (qumodes). Photons
displacing classical computing hardware? This article offers a status The infrastructure are naturally more robust to
update and a look ahead. thermal noise, and multiple
required to cool companies today are pro-
COOL TECHNOLOGY, ULTRA-COLD HARDWARE quantum computers ducing early-stage photonic
Quantum computers are cool; they exploit the subatomic phenom- quantum processors that do
ena of superposition and entanglement. Creating bits of information, has created a barrier not need cooling. QuiX is one
1s and 0s, at a quantum scale leads to an exponential advantage in example.
computational power. However, quantum systems are notoriously sus- to bringing quantum While scalable and versatile
ceptible to noise. Multiple sources of noise can reduce the accuracy of a computers to market, photonic hardware for quan-
computation or even entirely destroy quantum information. tum computing is still a ways
One of the most challenging noise sources to overcome is thermal but new approaches are off, some application-
noise. To avoid it, many popular hardware approaches are cooled to specific devices have already
ultra-cold temperatures. For example, superconducting quantum emerging. been realized. These include
computers require specialized vacuum pumps and cryostats. This machines from Orca
equipment is expensive, is dependent on helium and consumes consid- Computing that are capable of time-bin boson sampling, an approach
erable space, water and power. suited to machine learning and generative modeling.
To date, the infrastructure required to cool quantum computers However, the photonics-based approach to quantum computing is
has created a barrier to bringing quantum computers to our desk- not without its challenges. In some instances, detecting photons to
tops. However, new approaches to quantum computing are emerging, read out the solution to a quantum algorithm still depends on super-
including photonic and diamond-defect designs. The potential for cooled sensors. In other words, the qubits may be at room temperature,
these technologies to operate at room temperature could significantly but the technology to detect them is not. Also, the entangled light
Figure 1: Schematic for photonic quantum computing. Qubits can be stored and transmitted using light and manipulated with optical
elements.
MARCH 2023 | www.eetimes.eu