Page 39 - EE Times Europe November 2021 final
P. 39
EE|Times EUROPE 39
Tesla AI Day: What to Expect for the Future of Self-Driving Cars
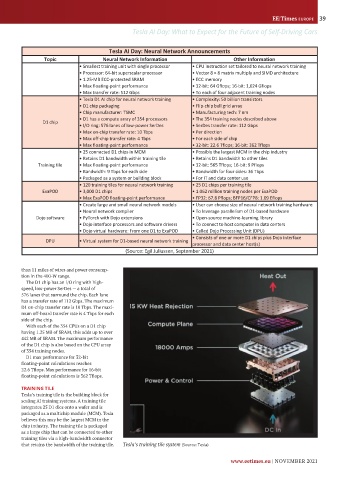
Tesla AI Day: Neural Network Announcements
Topic Neural Network Information Other Information
• Smallest training unit with single processor • CPU instruction set tailored to neural network training
• Processor: 64-bit superscalar processor • Vector 8 × 8 matrix multiply and SIMD architecture
• 1.25-MB ECC-protected SRAM • ECC memory
• Max floating-point performance • 32-bit: 64 Gflops; 16-bit: 1,024 Gflops
• Max transfer rate: 512 Gbps • To each of four adjacent training nodes
• Tesla D1 AI chip for neural network training • Complexity: 50 billion transistors
• D1 chip packaging • Flip-chip ball grid array
• Chip manufacturer: TSMC • Manufacturing tech: 7 nm
• D1 has a compute array of 354 processors • The 354 training nodes described above
D1 chip
• I/O ring: 576 lanes of low-power SerDes • SerDes transfer rate: 112 Gbps
• Max on-chip transfer rate: 10 Tbps • Per direction
• Max off-chip transfer rate: 4 Tbps • For each side of chip
• Max floating-point performance • 32-bit: 22.6 Tflops; 16-bit: 362 Tflops
• 25 connected D1 chips in MCM • Possibly the largest MCM in the chip industry
• Retains D1 bandwidth within training tile • Retains D1 bandwidth to other tiles
Training tile • Max floating-point performance • 32-bit: 565 Tflops; 16-bit: 9 Pflops
• Bandwidth: 9 Tbps for each side • Bandwidth for four sides: 36 Tbps
• Packaged as a system or building block • For IT and data center use
• 120 training tiles for neural network training • 25 D1 chips per training tile
ExaPOD • 3,000 D1 chips • 1.062 million training nodes per ExaPOD
• Max ExaPOD floating-point performance • FP32: 67.8 Pflops; BFP16/CFP8: 1.09 Eflops
• Create large and small neural network models • User can choose size of neural network training hardware
• Neural network compiler • To leverage parallelism of D1-based hardware
Dojo software • PyTorch with Dojo extensions • Open-source machine-learning library
• Dojo interface processors and software drivers • To connect to host computer in data centers
• Dojo virtual hardware: From one D1 to ExaPOD • Called Dojo Processing Unit (DPU)
• Consists of one or more D1 chips plus Dojo interface
DPU • Virtual system for D1-based neural network training
processor and data center host(s)
(Source: Egil Juliussen, September 2021)
than 11 miles of wires and power consump-
tion in the 400-W range.
The D1 chip has an I/O ring with high-
speed, low-power SerDes — a total of
576 lanes that surround the chip. Each lane
has a transfer rate of 112 Gbps. The maximum
D1 on-chip transfer rate is 10 Tbps. The maxi-
mum off-board transfer rate is 4 Tbps for each
side of the chip.
With each of the 354 CPUs on a D1 chip
having 1.25 MB of SRAM, this adds up to over
442 MB of SRAM. The maximum performance
of the D1 chip is also based on the CPU array
of 354 training nodes.
D1 max performance for 32-bit
floating-point calculations reaches
22.6 Tflops. Max performance for 16-bit
floating-point calculations is 362 Tflops.
TRAINING TILE
Tesla’s training tile is the building block for
scaling AI training systems. A training tile
integrates 25 D1 dies onto a wafer and is
packaged as a multichip module (MCM). Tesla
believes this may be the largest MCM in the
chip industry. The training tile is packaged
as a large chip that can be connected to other
training tiles via a high-bandwidth connector
that retains the bandwidth of the training tile. Tesla’s training tile system (Source: Tesla)
www.eetimes.eu | NOVEMBER 2021